
About This Quiz
There have been great inventors and scientists in every civilization throughout human history, but a confluence of favorable historical events means that a particularly high number of them popped up in the United Kingdom, particularly in the last several centuries. As an imperial power, Britain had a great deal of superfluous wealth flowing in, which sustained a growing and increasingly educated middle class, the key ingredient required to develop scientists and fund innovation. As new ideas, thinkers and institutions feed one another and more and more people are given access to the tools needed to create new ideas, the rate of innovation becomes faster and faster.
This means that some of the most important figures in the Industrial Revolution, the formation of the Information Age and the genetic revolution were found in Britain. They include key pioneers of the steam engine and the internet, as well as discoverers in fields as diverse as evolution and mathematics. They hailed primarily from the upper middle class, who had the education and connections necessary for study, but they were otherwise diverse, coming from all over the map and including men and women.
How many of these great innovators do you know? Let's find out!
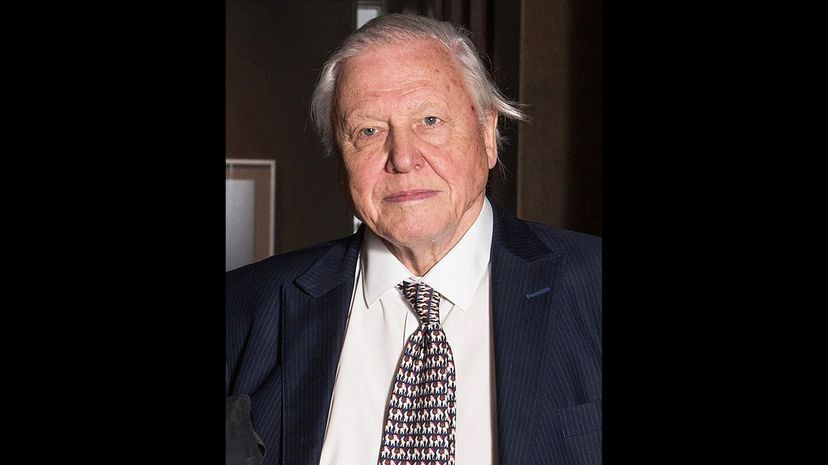

David Attenborough is that great thing, a science communicator who can illuminate the topic for laypeople. He was knighted for his services, and a major research ship recently launched that bears his name. He is an environmentalist, naturalist and conservationist who loves nature nearly as much as everyone in Britain loves him!

Thomas Crapper did not invent the flush toilet, but he made many improvements such as the ballcock and he marketed one of the first commercially successful lines of toilets. He is so successful that his name is literally a minor curse-word, although that word actually predates him. When he was born, however, it was probably considered quite a nice and innocent-sounding surname.
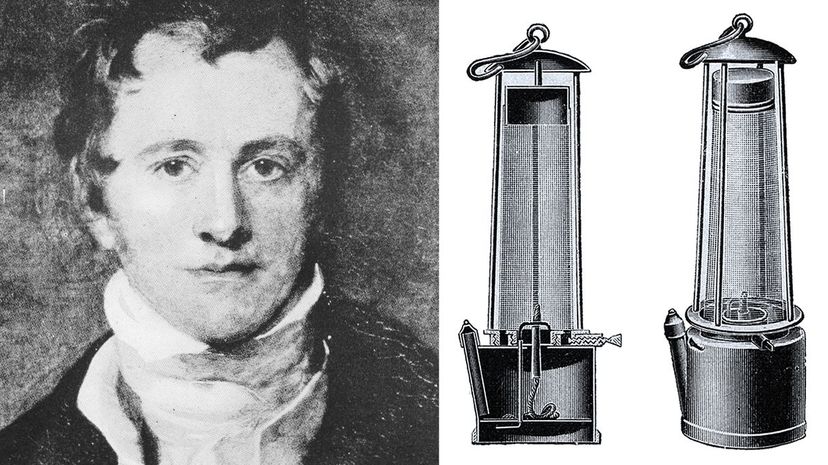
Humphry Davy was knighted for his contributions to science and also received an award from Napoleon during the Anglo-French conflict of the time. His major offering was that he replaced risky methane lamps with safer ones in mines, which saved many miners from horrible deaths. He also mentored Michael Faraday.
Advertisement
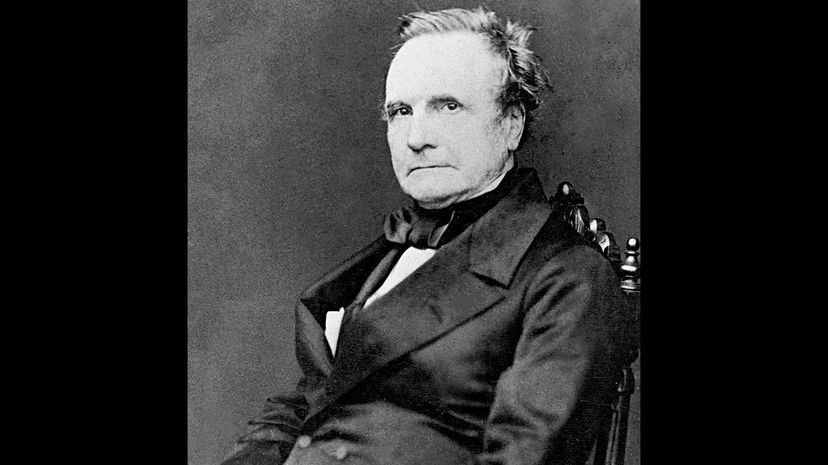

With his programmable punch card system that "programmed" looms and other weaving devices, Charles Babbage helped to create the first computer. Babbage was a sickly child who spent time reading since he couldn't do much else, making him a worthy grandfather to all modern nerds.
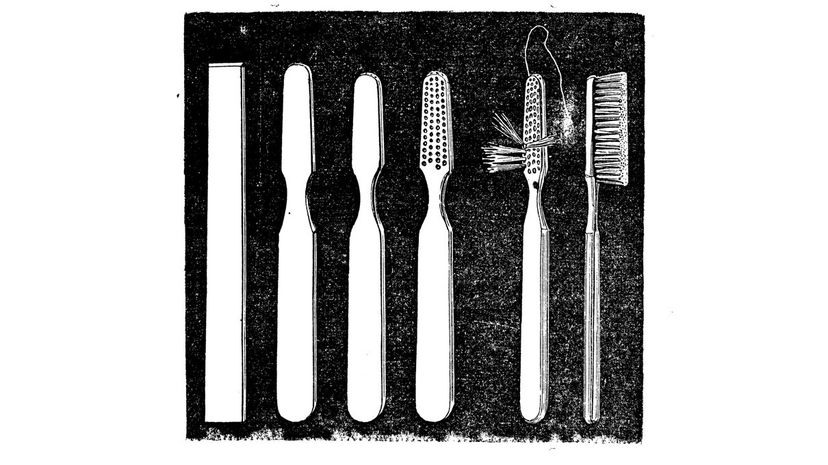
Toothbrushes did exist before they were mass-produced, but they were pretty awful, and since the mass importation of sugar, people's teeth really needed help. Enter William Addis, who invented his vastly superior brush around the same time that America was born.
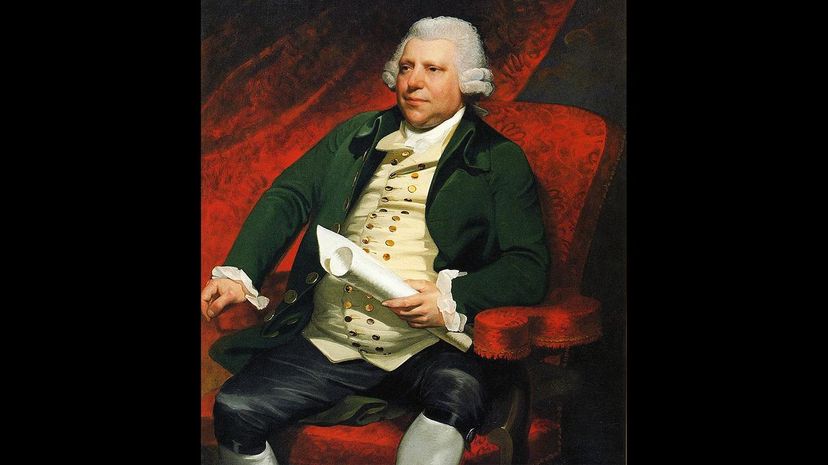

Before the Industrial Revolution, making fabric was a very slow and labor-intensive business. Richard Arkwright was not the inventor of the spinning jenny, the machine that transformed this process, but he did wildly improve the design. Without this innovation, producing enough clothing for the soaring population would have been borderline impossible without many more people becoming trapped in awful factory jobs.
Advertisement
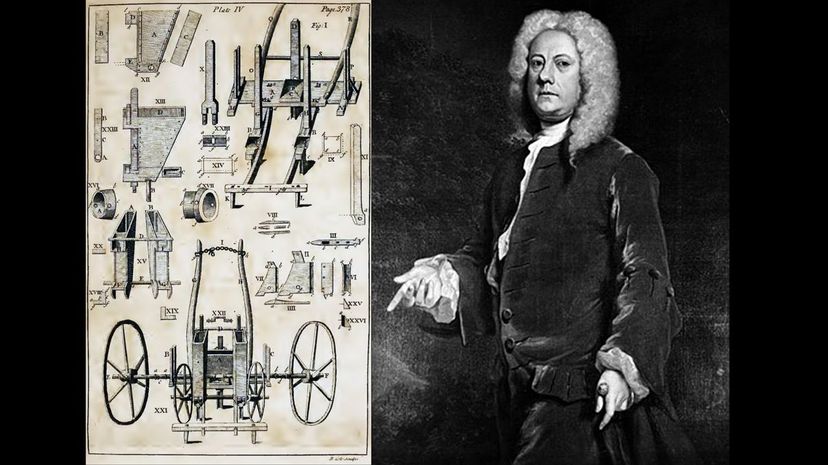
One problem with traditional agriculture was getting seeds into the ground far enough down to be safe from birds but not so far that they couldn't sprout and grow. Jethro Tull's seed drill solved this issue and was thus a key trigger for the Industrial Revolution.
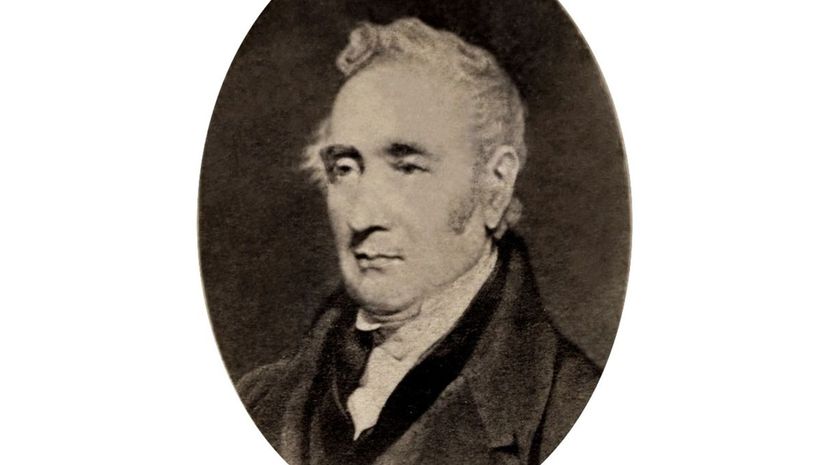

When George Stephenson's mechanic father used a Newcomen steam engine to pump water out of a mine, this inspired Stephenson's interest in steam. His first locomotive was for hauling coal, but he eventually built the first commercial moving locomotive and became "the Father of Railways".
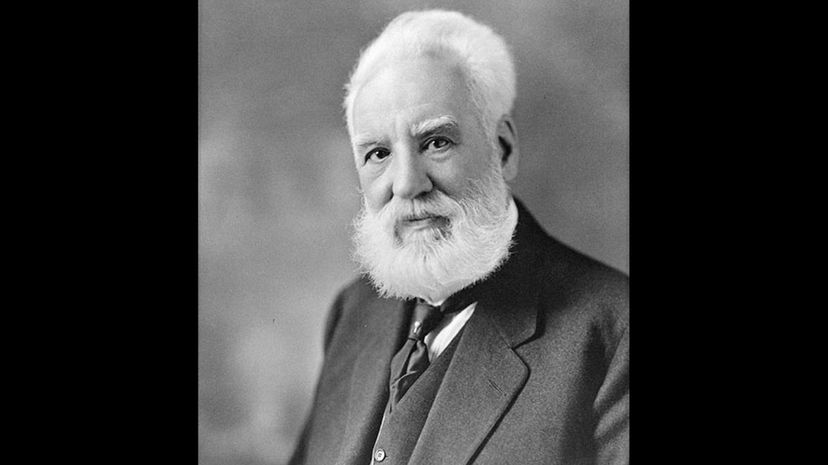

Inventor of the telephone, Alexander Graham Bell could not have foreseen how radically his invention would transform the world. Bell built on Joseph Stearns' work on the wire, which had enabled telegraph, and hired Thomas Edison to work with him on the telephone, which could transmit multiple messages through a single wire at once. The resulting patent is believed to be among the most valuable in history.
Advertisement
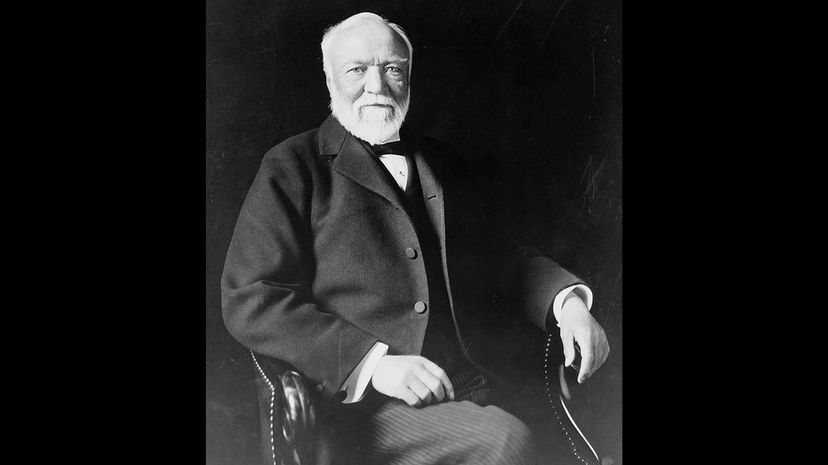

Andrew Carnegie is one of the so-called "Robber Barons" who got incredibly rich in the later 1800s by striking huge deals in steel, coal and other essential elements of the modern age. Carnegie later realized that his abuse of his workers wasn't a good look and endowed many libraries, purchasing a better legacy than his behavior deserved.
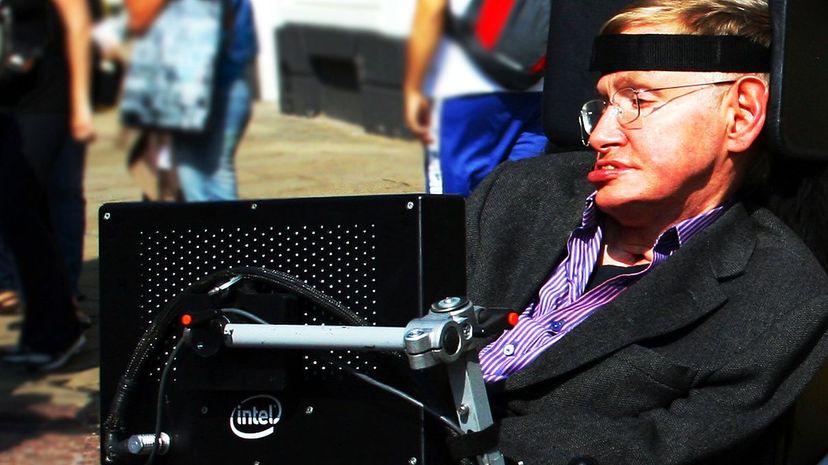

Stephen Hawking is one of the great minds of the 20th century, despite suffering from motor neuron disease which was expected to kill him in his 20s. He helped his field take huge strides toward a unified "Theory of Everything," building on the world of Albert Einstein.
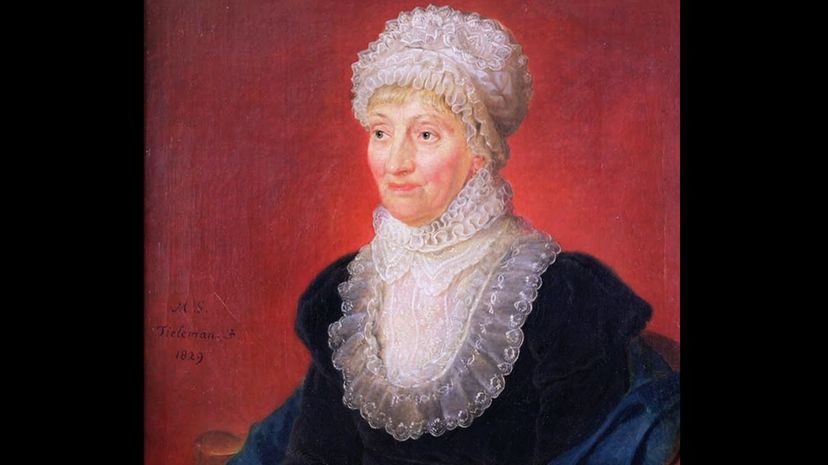

Caroline Herschel was born in Germany but married William Herschel, a British scientist. She became his teammate in all his work as a composer and astronomer and helped him discover the planet Uranus. She created new star charts and found several comets!
Advertisement
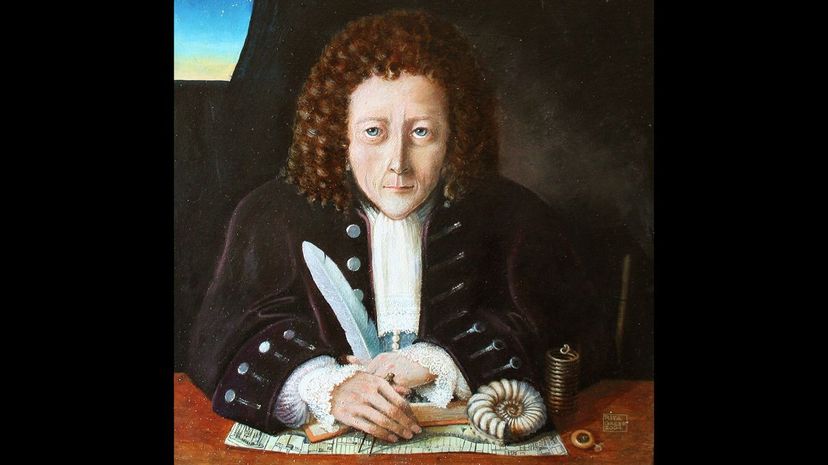

An English Civil War and Restoration-era man, Robert Hooke lived in the mid- to late 1600s and helped lay the groundwork of modern science. He figured out the law of elasticity, which is key to a great deal of later engineering innovation. In short, Hooke's Law tells you how stretchy or bouncy things are, and if you don't know that, it's very hard to build mighty bridges or machines with them!

Robert Boyle was the person who discovered that pressure can decrease the volume of a gas. This doesn't sound very exciting, as it's completely obvious, but it matters for two reasons: first, it had to be proved, and second, Boyle's method transformed the approach to science. Without his work, we might still be treating astrology and alchemy as equal to physics and chemistry.
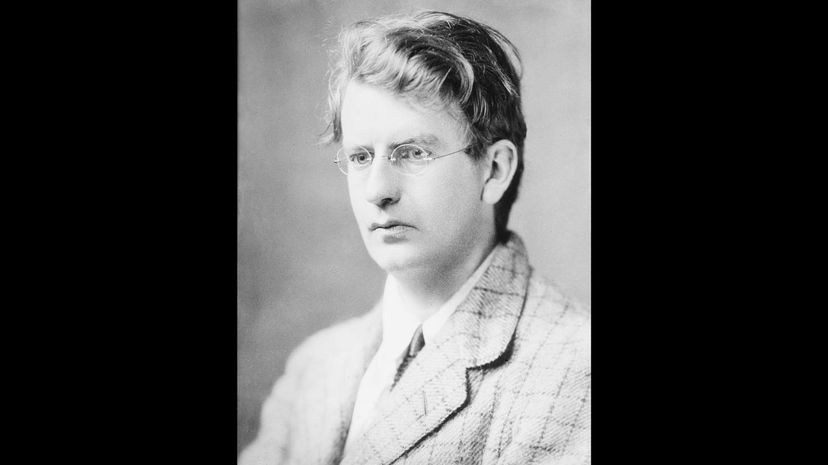

Even as the internet transforms what we consider to be television, it is beyond dispute that this device has been the most powerful mass communication medium since the invention of the written word. For that, we can thank Scotsman John Logie Baird, who created not just TV but also the first transatlantic broadcast and the first color TV.
Advertisement
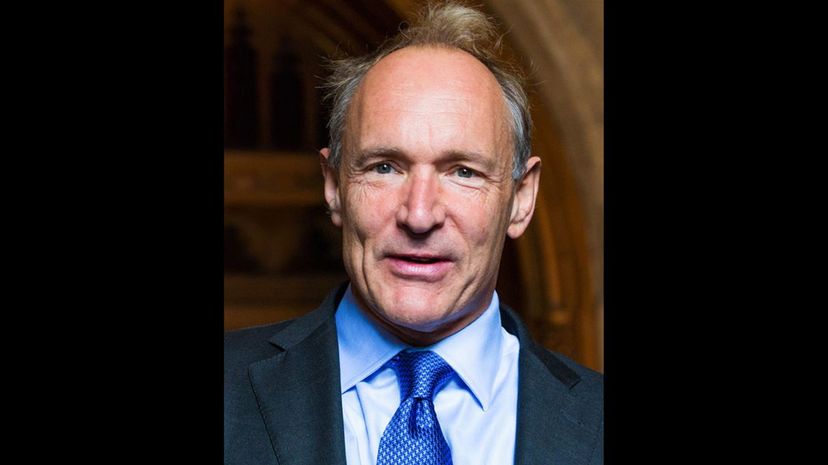

Sir Tim Berners-Lee is the father of the internet. He invented the World Wide Web while based at CERN, the Swiss laboratory where international scientists gather to cooperate. He created hypertext transfer protocol that enabled different computers to talk to one another. He also invented the server and the browser.
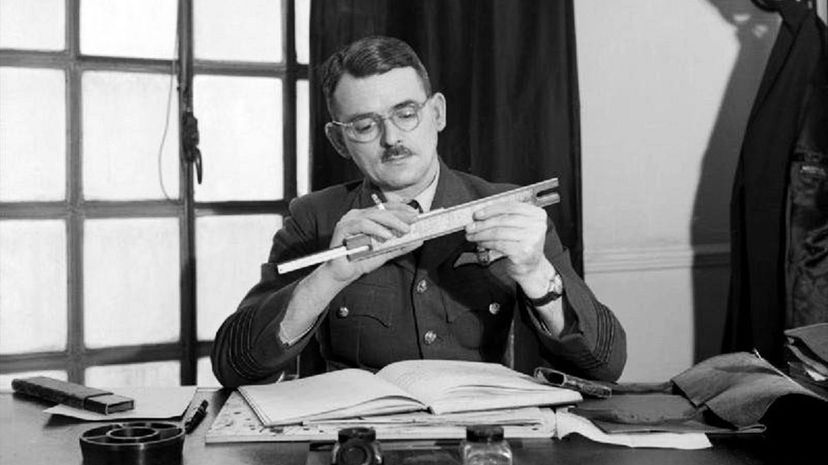

Frank Whittle was a giant of the aviation industry who helped to create a jet engine (though not the first, as one was developed in parallel in Germany) and then the turbojet. The British government invested in him thanks to World War II, and he lived until 1996, long enough to see his invention not just help the Allies win the war, but utterly transform the world.
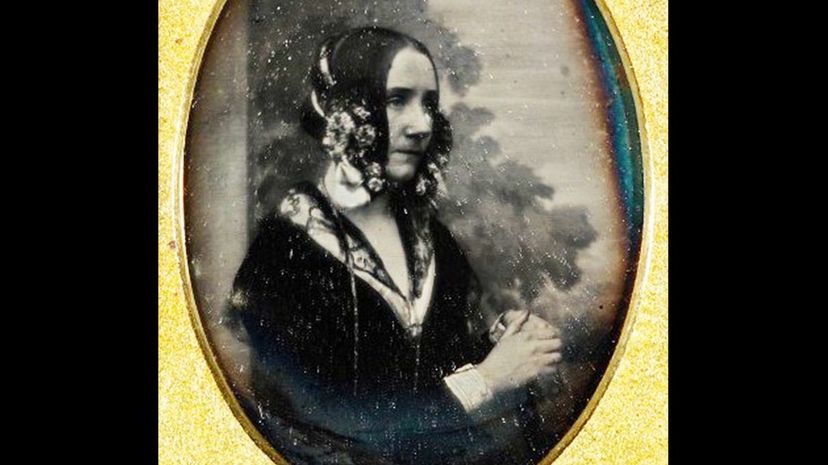

Ada Lovelace is the genius without whom Charles Babbage could never have built a computer. What she created is essentially the idea of code. She is the mother of programming, the person who made the software that makes the hardware actually work. She was also a countess!
Advertisement

Henry Cavendish came from the very powerful Cavendish family, which enabled him to fund a great education. He discovered the existence of the lightest element of all, hydrogen, which he called "flammable air," for which he won the Copley Medal.

Jocelyn Bell Burnell recently won the $3m Special Breakthrough Prize In Fundamental Physics, one of many honors she got for figuring out that mysterious regular "pulses" that telescopes detected coming from neutron stars were not, in fact, aliens (as many people believed). They were pulsars, a kind of fast-spinning star that gives off a detectable "pulse" thanks to its rotation.

Peter Higgs took home a Nobel Prize in 2013 for his work in predicting the existence of the Higgs boson, the so-called "God particle" that fills holes in the Theory of Relativity. Computers couldn't do the calculations when he first suggested it, but they caught up with his brain eventually. A massive "large hadron collider" was built at CERN to prove that the Higgs boson was real, and while it took years and billions of dollars, it eventually worked. Higgs was 83, and very glad to live to see himself proved right.
Advertisement

A Regency-era scientist, Mary Anning got her initial training by scouring the fossil cliffs at Lyme Regis, near her home. She sold fossils to make a living and began to write about her discoveries. She became quite well-known in paleontology but never achieved full recognition due to her gender. Her biggest find was the discovery of the very first plesiosaur!

James Watson was part of the key four scientists (all named above) who discovered the double helix structure of the DNA molecule, the secret of life. Watson and his partner Crick stole some key materials from Franklin, thus they share the discovery with her, as well as with her colleague Wilkins.
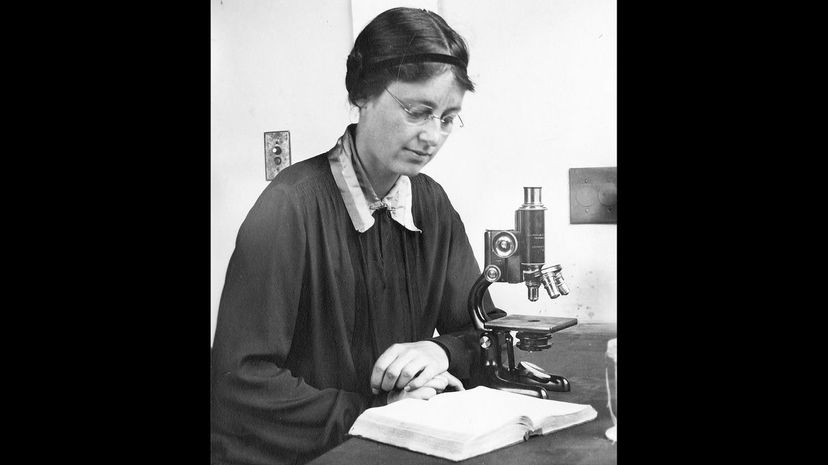

Kathleen Mary Drew-Baker was a phycologist, meaning that she studied algae. She graduated from university in 1923, at a time that it was rare for women to be allowed in, and won a fellowship to study cryptogamic botany. Much of what we know about seaweed is thanks to her, and indeed without her work on the commercialization of seaweed production, it is very unlikely that sushi could have continued to keep pace with population growth.
Advertisement
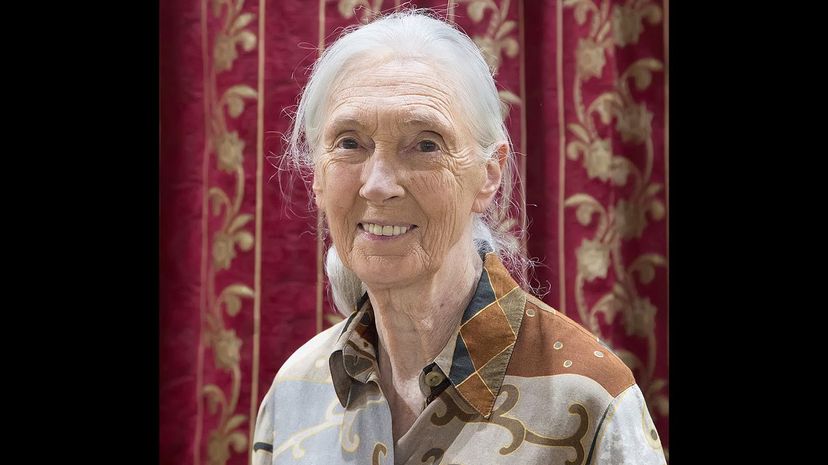

Jane Goodall is a great British naturalist who is famous for her work protecting habitats and understanding humanity's closest cousins. She has transformed our knowledge of primates, and not only that, she is also a great communicator who was able to make the public understand the importance of her work and commit to supportin it.
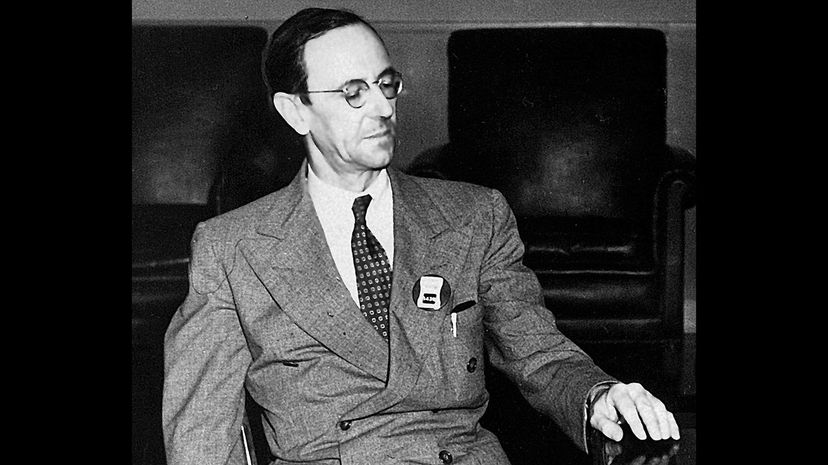

Born in Cheshire, James Chadwick won the Nobel Prize for discovering the neutron, the neutral particle that explains the mass of atoms. He also wrote a key research paper that helped the US government get the atom bomb before the Nazis, thus helping the Allies win World War II.
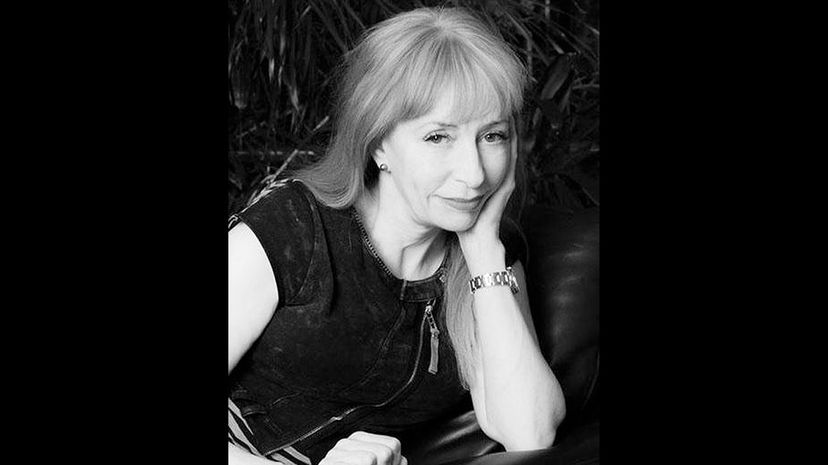

Dr. Susan Greenfield is now a baroness thanks to her contributions to neuroscience. She has a high profile as a great science communicator, and is noted for her books on the nature of the mind and consciousness.
Advertisement
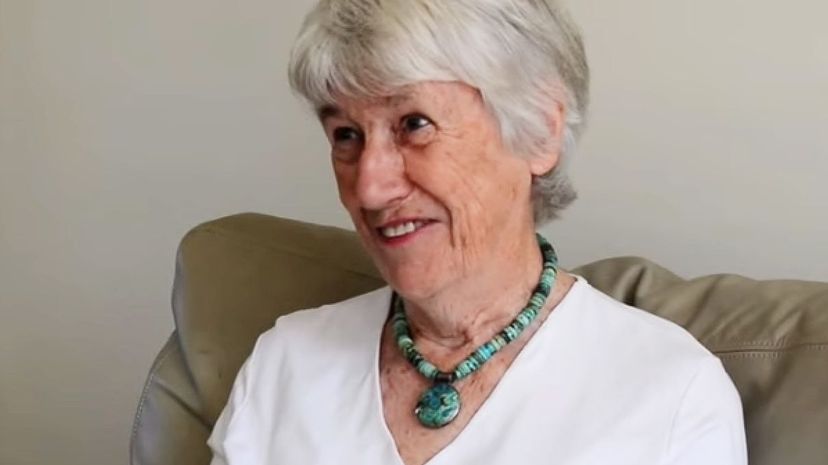

Bridget Ogilvie is a member of the Royal Society who shed a tremendous amount of light on how the immune system handles parasites that enter the body. She is also noted for being a great science communicator and won a knighthood for her work.
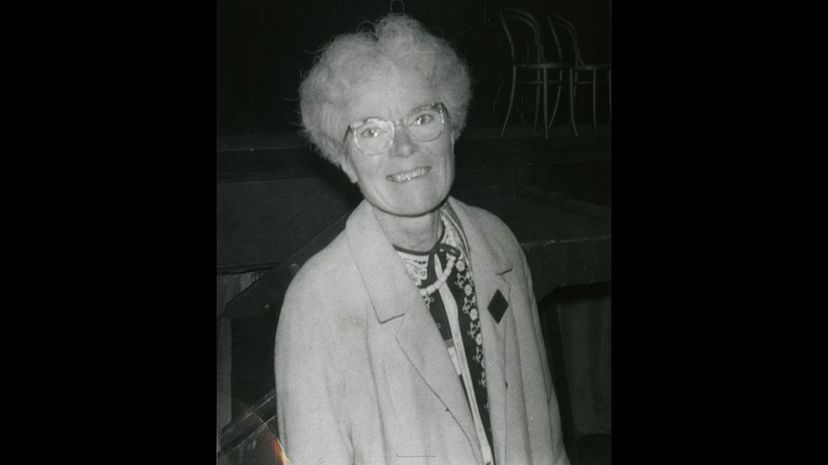

Kathleen Lonsdale helped to create the science of crystallography, among other contributions to both physics and chemistry. She worked at University College, London, and helped to uncover the structure of many chemicals, as well as how to make synthetic diamonds. A type of diamond that only exists in meteorites is named in her honor—Lonsdaleite!
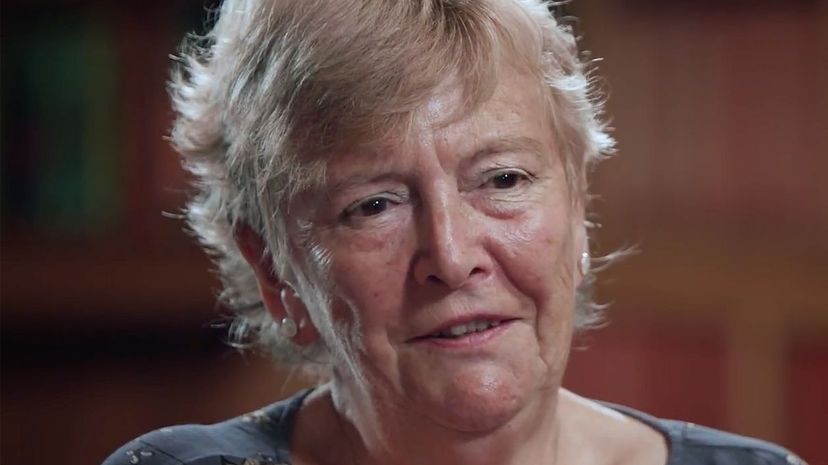

Professor Julia Higgins, now also known as Dame Julia, is a leader in the field of polymers. These are substances made of many molecules of similar units, and typically include a lot of types of plastic, meaning that better research is essential to improved food security, reducing pollution and other things.
Advertisement
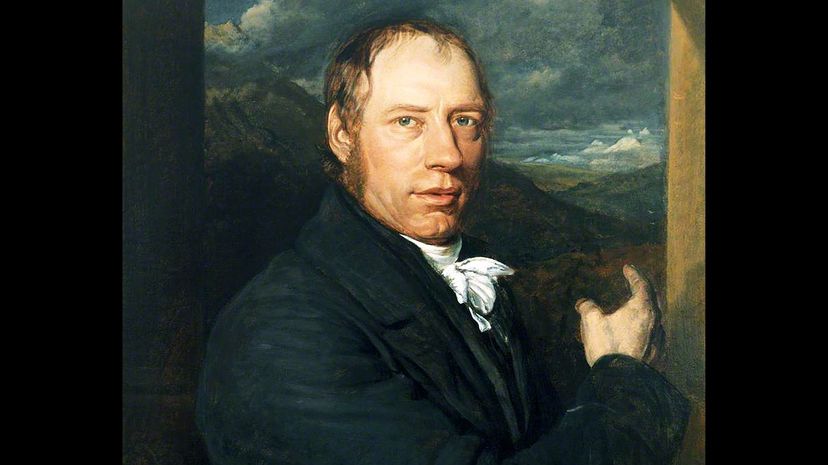

This "giant of steam" was probably born a little too early. He invented the first steam-powered locomotive, but because nobody had built adequate railways for it yet, they didn't really appreciate it. He lived a rather sad life and never made much money from it. If he'd shown up even 30 years later, he would have been in solid company, instead of a more lonely voice in the scientific wilderness!
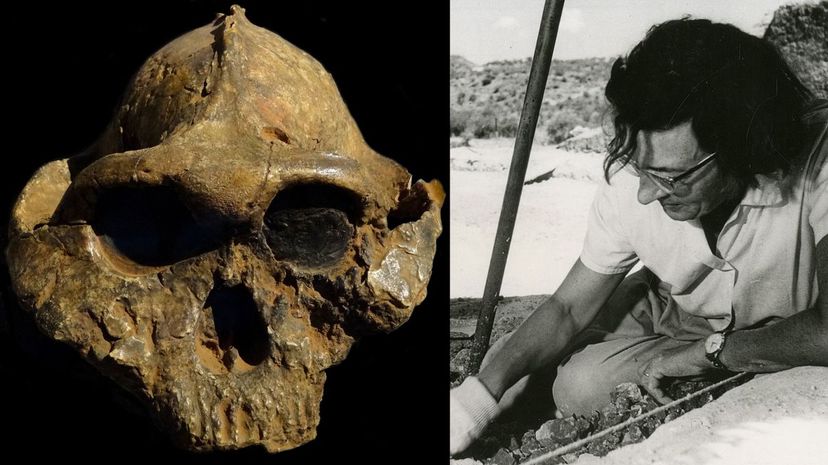

Mary Leakey was involved in excavations all over England and then in East Africa, studying ancient pottery and tools. She wrote a beautiful book called "Africa's Vanishing Art" that helped her fellow Westerners understand that "the dark continent" was horribly misnamed. She was primarily known for her uncanny talent for finding quality fossils.
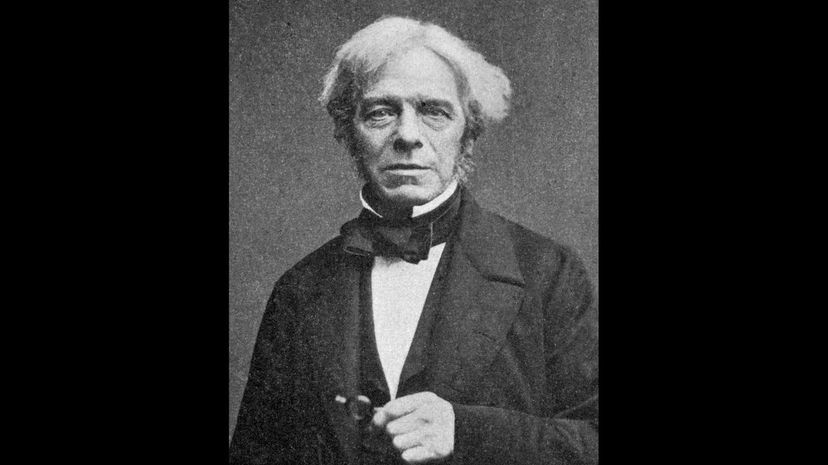

Faraday is unusual as he was born poor, but managed to get educated through his job as an apprentice bookbinder. He discovered electromagnetic induction, which led to the invention of the transformer and the generator. Next time you push an "on" switch and something happens, you'll know who to thank!
Advertisement
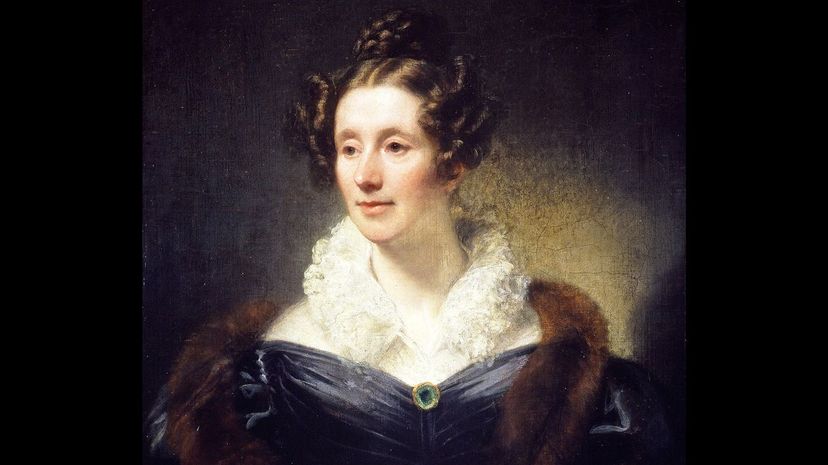

Mary Somerville was a scientist who wrote all about light, magnetism, mathematics and astronomy. She was jointly the first woman to join the Royal Society, even though they did take their time to acknowledge her. She also discovered two new comets!
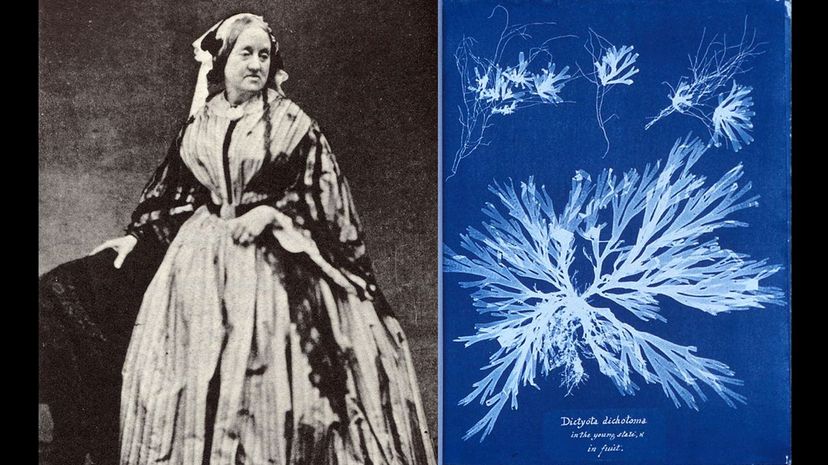

Possibly the first female photographer, Anna Atkins was an artist and engraver specializing in botany. She is particularly noted for her work on "sun-printing," a new method of creating photographs, which led to her plant book, "Photographs of British Algae: Cyanotype Impressions". She was an early female member of the Botanical Society of London.
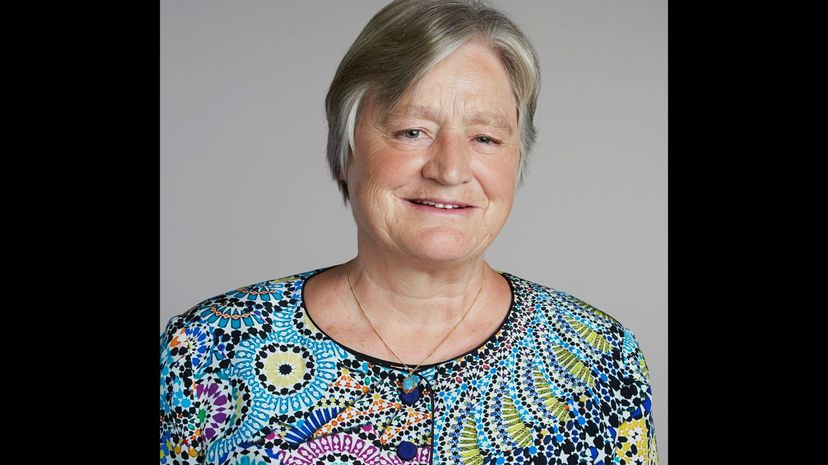

Dame Julia Slingo's work is important enough to earn her a knighthood. She was previously Director of Climate Research in NERC's National Centre for Atmospheric Science at the University of Reading, and she has been particularly insightful in creating accurate climate models that tell us exactly what to expect (and they keep being proven right).
Advertisement
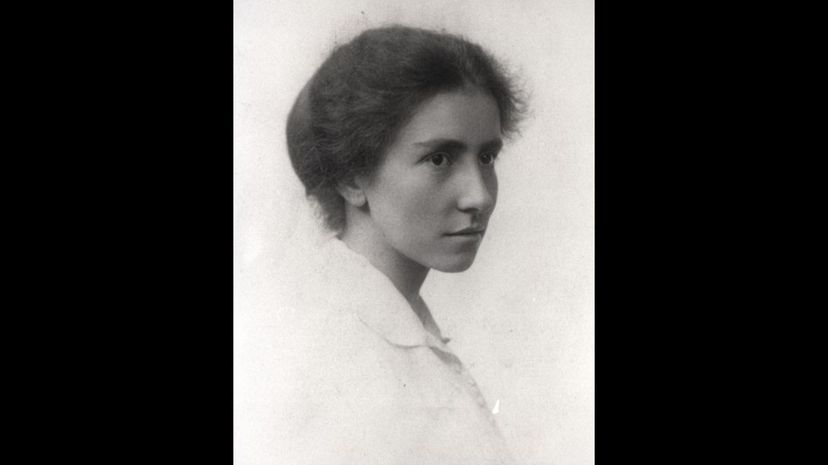

Professor Garrod was the first woman to be a full professor at Cambridge University, and the first female department chair. Garrod excavated many skeletons that shed light on the relationship between human and Neanderthal, and helped us understand how we became who we are.
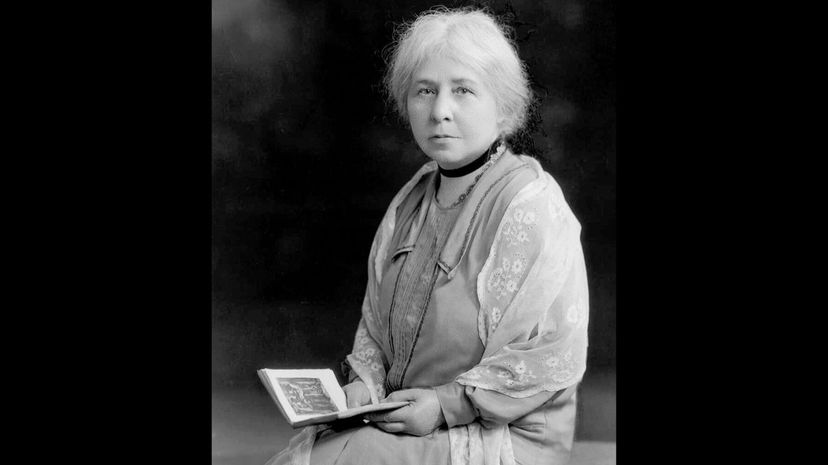

Born in India under British rule, Murray was an important figure in archaeology and the first woman to lecture at University College, London. She rather went off-script with her "witch cult" theory that suggested many of the people burned as witches were in fact merely latter-day pagans, which is not confirmed but inspired an awful lot of interesting fiction.

Hertha Ayrton was a Jewish physicist who was a trailblazer for other women in science. She worked on electric arcs, building a better light. She was rejected from the Royal Society because she was a woman, but won the prestigious Hughes Medal. She also invented the Ayrton Flapper Fan, which saved lives in World War I when it cleared poison gas from trenches. Her husband said to a cousin, "You and I are able people, but Hertha is a genius."
Advertisement
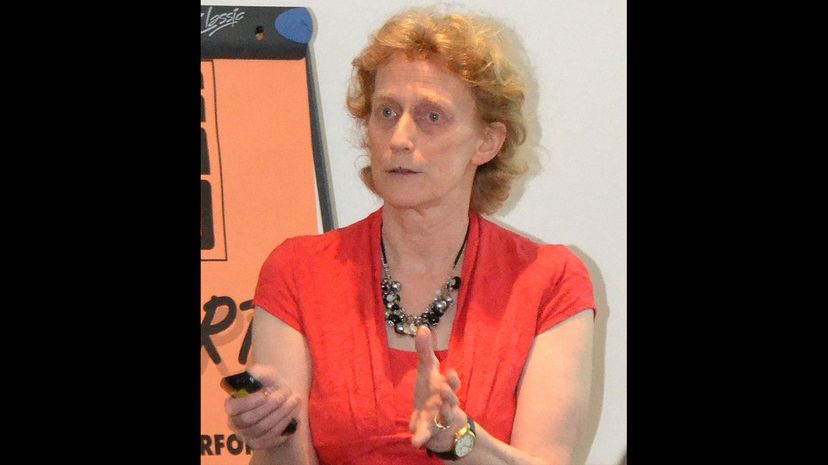

Athene Donald is a leading light in the fields of Biological and Soft Systems—that is the combining of biological and synthetic systems. She is the Master of Churchill College, Camridge, and a member of the Royal Society.